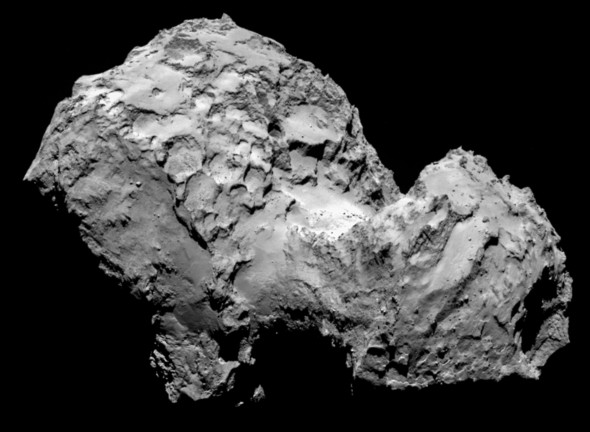
comet 67p
today satellite ‘rosetta’ delivers and enables landing pod ‘philae’ a first for mankind: landing on a comet-comet 67p/churyumov-gerasimenko. the feat, landing in a precise preordained spot is akin to a bullet landing on another bullet. it launched in 2004 traveling four billion miles rocketing at 21,000 mph, the comet 83,889 mph.
“we are on the comet,” stephan ulamec, philae lander manager, announced wednesday 12 november 2014, marking a historic achievement.
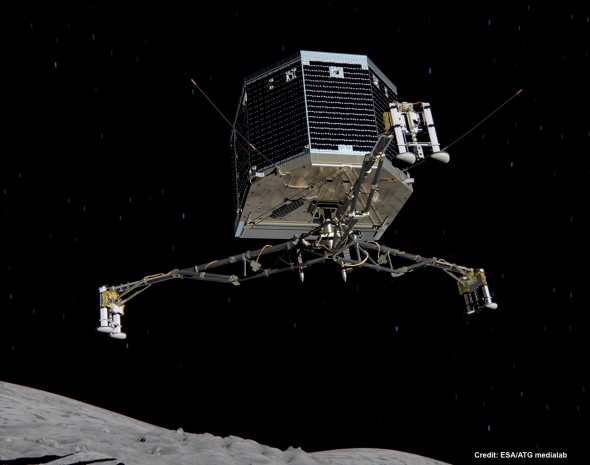

above> philae landing pod – simulation | below> satellite rosetta philae landing pod – simulation


above> the first image the esa released from the philae lander shows the craft breaking away from the rosetta orbiter and heading toward 67p | below> rosetta’s camera catches philae descending towards 67p


above> the philae lander took this photo of its descent onto comet 67p wednesday, when it was about 3 kilometers from the surface. the landing site is seen with a resolution of about 3 meters per pixel | esa/rosetta/philae/rolis
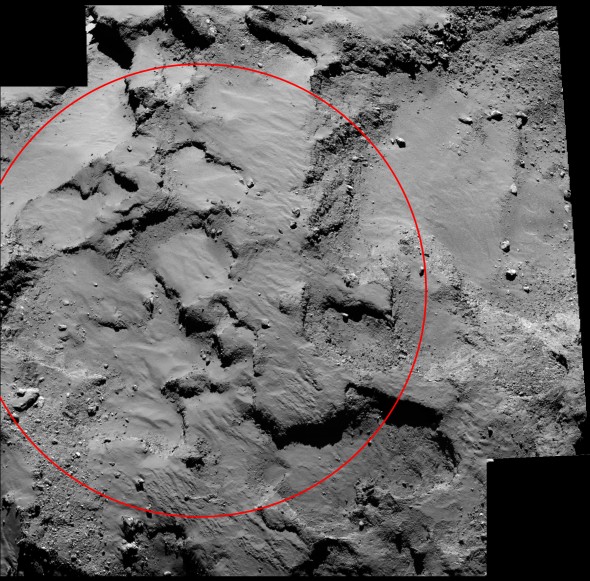

above> a close-up view of philae’s landing site on the comet. the red circle is about 500 meters, or 1,640 feet, across for scale. credits: esa/rosetta/mps for osiris team mps/upd/lam/iaa/sso/inta/upm/dasp/ida
above> date> 02 january 2014 | satellite> rosetta | depicts> philae lander | copyright> esa/atg medialab
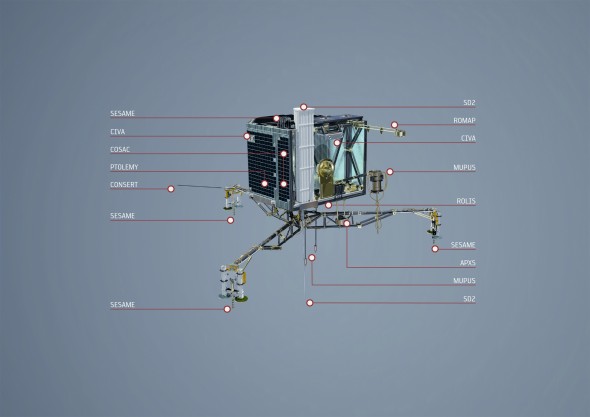
rosetta will deploy the philae lander to the surface of comet 67p/churyumov-gerasimenko for in situ analysis with its 10 instruments:
APXS: alpha proton x-ray spectrometer (studying the chemical composition of the landing site and its potential alteration during the comet’s approach to the sun)
CIVA: comet nucleus infrared and visible analyser (six cameras to take panoramic pictures of the comet surface)
CONSERT: comet nucleus sounding experiment by radiowave transmission (studying the internal structure of the comet nucleus with rosetta orbiter)
COSAC: the cometary sampling and composition experiment (detecting and identifying complex organic molecules)
PTOLEMY: using modulus protocol (methods of determining and understanding light elements from unequivocal stable isotope compositions) to understand the geochemistry of light elements, such as hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen and oxygen
MUPUS: multi-purpose sensors for surface and sub-surface science (studying the properties of the comet surface and immediate sub-surface)
ROLIS: rosetta lander imaging system (providing the first close-up images of the landing site)
ROMAP: rosetta lander magnetometer and plasma monitor (studying the magnetic field and plasma environment of the comet)
SD2: sampling, drilling and distribution subsystem (drilling up to 23 cm depth and delivering material to onboard instruments for analysis)
SESAME: surface electric sounding and acoustic monitoring experiment (probing the mechanical and electrical parameters of the comet), comprising: casse (comet acoustic surface sounding experiment), dim (dust impact monitor), and pp (permittivity probe).
with a cost of 200 million euros — or about $250 million — the lander will provide ground truth for groundbreaking observations already underway by rosetta. the chief goal of the $1.7 billion rosetta mission is to find out how comets work and whether they may have seeded earth with water and the building blocks for life — like organic molecules, amino acids, and other life-forming material. [ watch esa live stream ]
[ esa ][ esa top 10 at 10 km ][ npr ]
update> there were some problems upon landing: in an update from the lcc in esa’s live stream at 5:42 est, it was announced that analysis of telemetry indicated that the landing was softer than expected, that the harpoons had not fired upon landing, and that the thruster had not worked.
1> philae details
2> finding a landing spot is hard to do
3> size comparison: 67p and paris





